Transparent
Co3FeOx Film Passivated
BiVO4 Photoanode for Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting
FANG Ming, QIN Qi, CAI Qian and LIU Wei*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1505-1512 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3162
December 15, 2021
photoelectrochemical water splitting, bismuth vanadate, co-catalyst, cobalt-iron oxide
ABSTRACT
Photoelectrochemistry that
use semiconductors to absorb sunlight for water splitting provides an effective
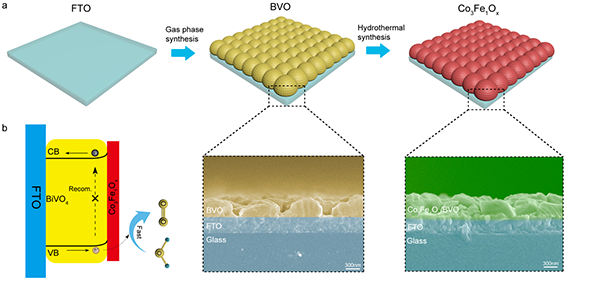
method for the development of renewable hydrogen energy in the future. In this paper, a transparent and highly-efficient cobalt-iron oxide (Co3FeOx) nano-film was fabricated through hydrothermal method by
directional adjustment of atomic ratio to promote the kinetics of BiVO4 (BVO) photoanode water oxidation. As a result, the Co3FeOx-modified BVO photoanode (Co3FeOx/BVO) exhibits an impressive
photocurrent density of 4.0 mA·cm-2 at 1.23 V versus reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE), approximately 2.17-fold
higher than that of bare BVO, as well as a cathodically shifted onset potential
of 320 mV. Transparent
catalyst nanolayer structure is clarified by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. In
addition, the Co3FeOx/BVO
photoanode has better stability, and there is no obvious activity degradation
after 10 hours of reaction. This strategy provides a broad prospect for the use
of water oxidation co-catalyst to achieve effective water splitting.