Cover Picture
Ultrathin ZnIn2S4 Nanosheets
Supported Metallic Ni3FeN for Photocatalytic Coupled Selective
Alcohol Oxidation and H2 Evolution
Mengqing Li, Weiliang Qi, Jiuyang Yu, Lijuan Shen, Xuhui Yang, Siqi Liu* and Min-Quan Yang*
Submit a ManuscriptEngineering the Interface and Interaction Structure on Highly Coke-Resistant Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 Catalyst for Dry Reforming of Methane
Sha Li, Xin Wang, Min Cao, Jingjun Lu, Li Qiu and Xiaoliang Yan*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2212007-2212014 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0113
December 2, 2022
metal-support interaction, interface, Ni catalysts, CeO2, dry reforming of methane
ABSTRACT
Designing
and tailoring metal-support interaction in Ni-based catalysts with plentiful
interfacial sites is of significant interest for achieving a targeted catalytic
performance in dry reforming of methane (DRM), but remains as a challenging
task. In this work, Ni/Al2O3 and Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts with the same strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) but distinct
interface structure are developed by an improved evaporation-induced
self-assembly method using pseudobohemite gel as aluminum source. Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 exhibits superior catalytic activity and stability in DRM in comparison with
Ni/Al2O3. The highest CH4 and CO2 conversion reaches at 71.4% and 82.1% for Ni/CeO2-Al2O3,
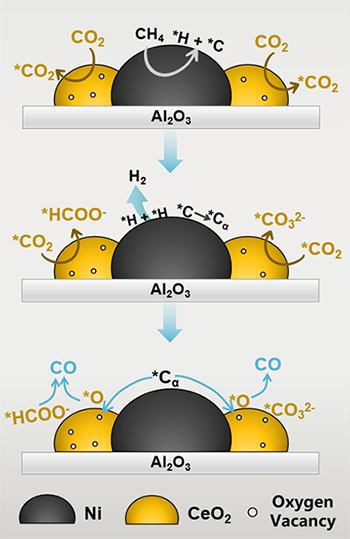
which are higher than that of 64.3% and 75.6% for Ni/Al2O3 at 700 °C. The SMSI effect in Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 provides more active interfacial sites with less coke deposition, and promotes
the generation of active formate species which are the key intermediates for
DRM. The findings of the present work could possibly pave the way for
fabricating catalysts with SMSI strategy for efficient heterogeneous catalysis.