Just Accepted

Zhilin Meng, Haiying Lu, Weijie Li*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100800
ABSTRACT
The
significance of these advances can be highlighted in four aspects. First,
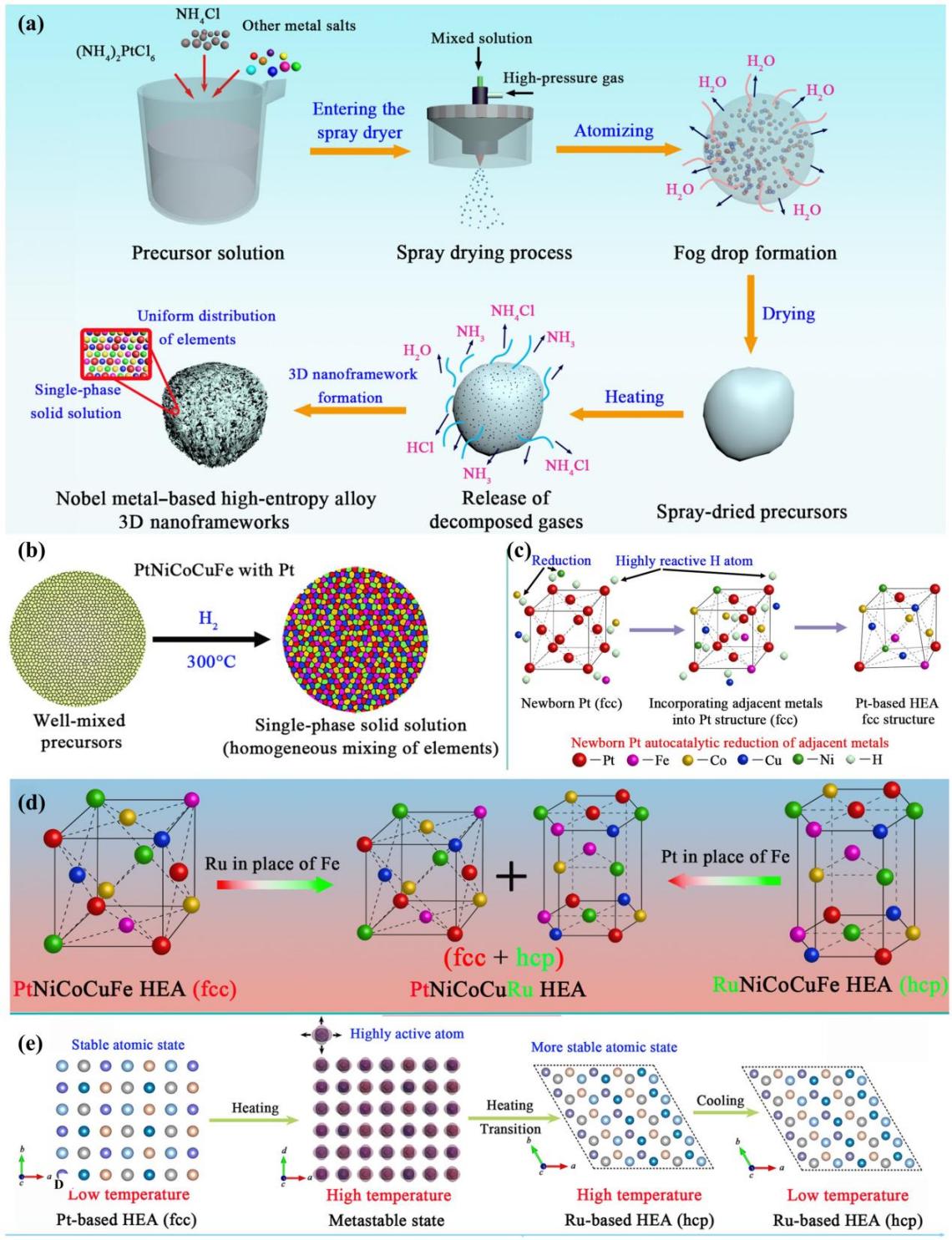
SD-TDR demonstrates a universally applicable, low-energy and surfactant-free
pathway for synthesizing HEAs with atomic-level homogeneity, addressing
long-standing synthesis challenges. Second, the autocatalytic mechanism and
elemental-specific role (Pt, Ir, Ru vs. Pd) provide a new theoretical framework
for understanding phase formation and multi-element synergy. Third, the precise
control over crystal structure (fcc/hcp) introduces a powerful lever for
optimizing catalytic pathways by exposing diverse crystal surfaces and active
sites, atomically deciphering the "cocktail effect" in HEAs.
Crucially, these structural innovations translate into exceptional catalytic
performance. PtNiCoCuRuIr nano-frameworks exhibit methanol oxidation activities
nearly 15 times higher than commercial Pt black, underscoring the practical
promise of this approach. By integrating mechanistic clarity with synthetic
precision, it redefines the design space of HEAs and opens the way toward
extending these strategies to non-noble systems, paving the path for the discovery
of multifunctional catalysts across future energy technologies.