Just Accepted
Just Accepted Articles have been posted online after technical editing and typesetting for immediate view. The final edited version with page numbers will appear in the Current Issue soon.
Submit a Manuscript

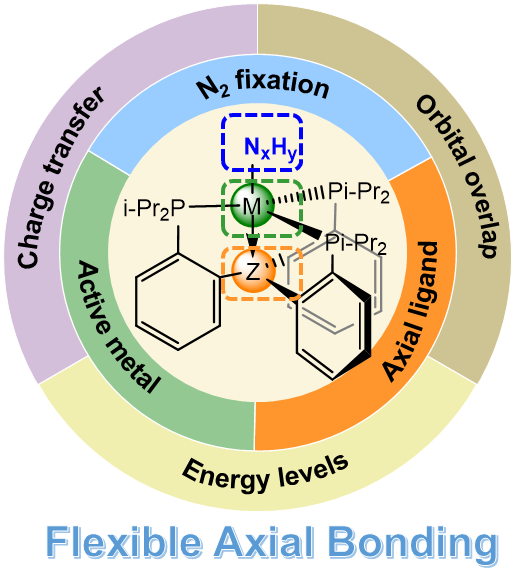
Dinitrogen fixation on transition metal complexes with flexible axial bonding
Xue-Lu Ma*, Jun-Bo Lu, Yuan Zhang, Ya-Fei Jiang, Jun Li *
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100831
ABSTRACT
The conversion of molecular dinitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3) is one of the most important chemical processes. The hemilabile axial bonding in the transition metal (TM) complexes with d-p, d-d and d-df interactions could provide an electron reservoir that controls the evolution of the oxidation state on the active center, which is potential to facilitate N2-to-NH3 conversion. In this perspective, the bionic nitrogen fixing process is illustrated on a molecular level, which features flexible axial bonding to regulate “electron reservoir”. The comprehensive overview summarizes the features of TM complexes with axial supporting ligand and focuses on how the axial ‘‘assistant” atom tunes the electronic properties of the metal center to facilitate dinitrogen binding, as well as proton/electron delivery in N2 reduction. To illustrate the mechanism of axial ‘‘electron reservoir” in dinitrogen fixation on different TM complexes with axial supporting ligand, the relationships of geometric parameters, the variation of electronic structure and oxidation state, the influence principles of axial bonding regulated by anchor atoms, the critical roles of peripheral ligands and the overall comprehension from orbital interaction are all involved. A preliminary view of the major challenges and future opportunities of TM dinitrogen complexes with flexible axial bonding is highlighted at the end. Through this perspective, we hope to give a comprehensive demonstration of the flexible axial bonding as “electron reservoir” in dinitrogen fixation, and shed light on the rational design for fabricating efficient catalysts in the future.