Just Accepted
Just Accepted Articles have been posted online after technical editing and typesetting for immediate view. The final edited version with page numbers will appear in the Current Issue soon.
Submit a Manuscript

Engineering 2D/2D FeOOH/BiOCl S-scheme heterojunction toward efficient and stable tetracycline photodegradation
Wanxin Hu, Yan Shi, Junxia Yu, Haiyang Shi*, Yingping Huang, Ruiping Li*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100832
S-scheme heterojunction; BiOCl; Photocatalysis; Charge separation; Structural stability
ABSTRACT
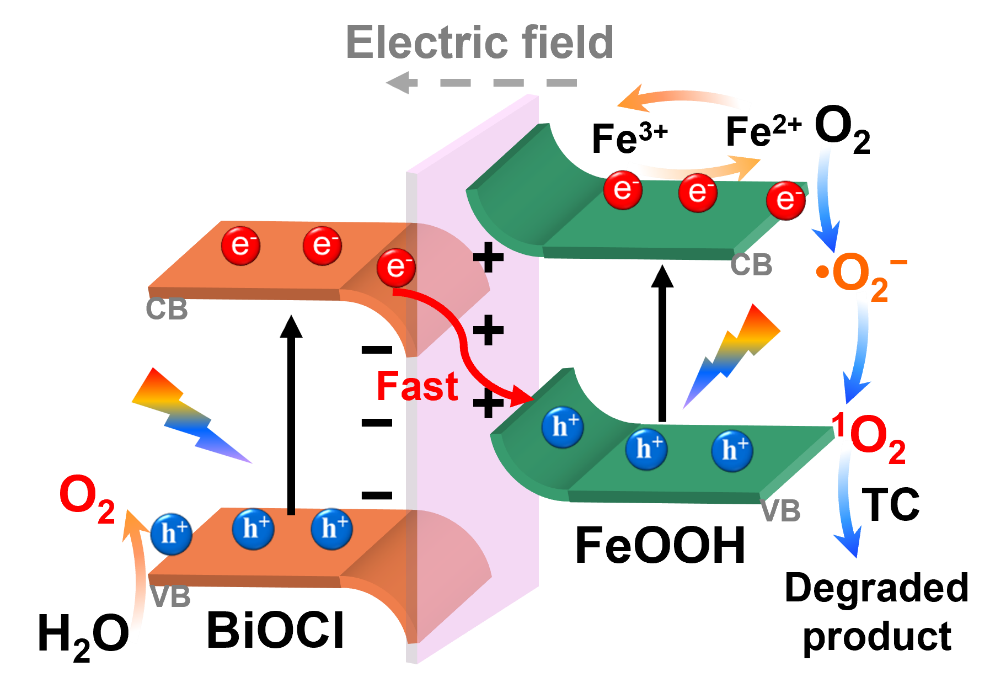
Layered BiOCl photocatalyst exhibits great promise for photocatalytic wastewater treatment in environmental remediation. However, its structural instability hinders further development toward photodegrading organic pollutants due to the photocorrosion caused by slow photocarrier separation. To address this major challenge, the constructed BiOCl-based S-scheme heterojunction is considered as one wonderful strategy which can efficiently steer photocarrier separation by the internal electric field and synergistically achieve stable surface structure. In this work, 2D/2D FeOOH/BiOCl S-scheme heterojunction by coupling FeOOH and BiOCl nanoplate was prepared via in situ photodeposition approach. Photocatalytic results indicate that the optimal 10 wt% FeOOH/BiOCl exhibits excellent photocatalytic activity and stability in tetracycline (TC) degradation, obtaining over 89.14% photodegradation efficiency with a kinetic constant of 0.024 min−1, which is 5.2 times higher than that of bare BiOCl (0.0046 min−1). Moreover, based on the results of cycle experiment and structural characterization, FeOOH-modified BiOCl still maintains nearly 80% photodegradation efficiency after cyclic reaction, significantly boosting photocarrier separation rate and improving structural stability of BiOCl crystal. The present study offers a novel strategy for stabilizing oxyhalide crystals by construction of S-scheme heterojunction, enabling effective photodegradation of organic pollutants.