Just Accepted

Weiming Lai, Yangyang Wan*, Kai Yan*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2026.100906
ABSTRACT
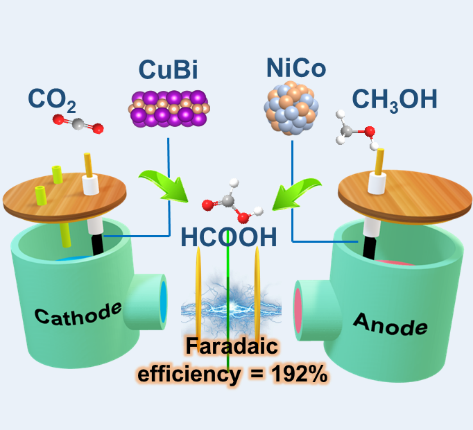
This work highlights the immense
potential of coupled electrocatalysis for low-energy CO2 utilization
and the production of value-added chemicals. By simultaneously converting CO2 and methanol into formic acid at both electrodes, the system effectively
utilizes the energy from renewable electricity to generate a high-value
product. The use of alloy catalysts to promote selective intermediate formation
and suppress competing pathways plays a crucial role in the success of the system,
providing a clear example of how material design can overcome the limitations
of conventional catalytic processes. The integration of CO2 reduction with methanol oxidation represents a novel approach to coupled
electrocatalysis that maximizes the potential of both reactions, offering a
path toward more efficient and sustainable chemical processes. As the field
continues to evolve, such innovative strategies will be essential in realizing
the full potential of electrochemical CO2 utilization for a sustainable
future.